There are two standards governing EV charging. In the U.S. there is the SAE J1772 standard, while in Europe and China the IEC61851 standard is used.
Solutions for E-Mobility Demands
Contributed by | Zettler New Energy Solutions
Introduction
Innovation and leading-edge product development have always been a hallmark of ZETTLER Group’s engineering competence. During recent years, this has been particularly evident by our leadership role in providing component solutions in the field of Alternative and Renewable Energy and by developing special electromechanical switching devices for these types of applications.
As electro mobility and other alternative transportation technologies continue to grow globally, ZETTLERs NEW ENERGY SOLUTIONS division is committed to supporting customers in electro mobility sectors around the world, with first-class engineering and new product design, and by leveraging ZETTLER Groups worldwide production and distribution resources.
ZETTLERs industry-leading electromechanical ‘new energy’ components are designed for use in electric vehicle charging devices, electric drive trains or any similar applications requiring high loads to be switched and carried.
E-mobility charging – IEC61851 modes and SAE J1772 levels
There are two standards governing EV charging. In the U.S. there is the SAE J1772 standard, while in Europe and China the IEC61851 standard is used. The IEC standard was derived from the SAE standard and thus has similar requirements, adapted for the European and Asian AC line voltages. Most terminology differences are small. While the SAE standard describes METHODS and LEVELS, the IEC standard talks about MODES, which are virtually the same.
The charging of electro vehicles may take place in different manners, either with 1 or 3 phase household level AC voltages and respective currents, or by use of DC quick charging at voltages of 200 to 600V at currents up to 400A.
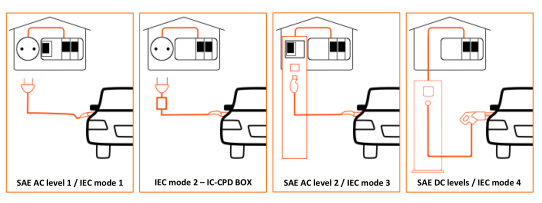
SAE AC level 1: Level 1 Charging utilizes a direct cable connection between the EV and a standard 1 phase 120V AC wall outlet. The outlet has to be protected by a circuit breaker and ground fault interrupter (GFI)/residual current detector (RCD). Charging power of 1.9 kW can be achieved.
SAE AC level 2: This is charging with 1 or 3 phase AC by use of a stationary charging station which is protected by a circuit breaker and GFI/RCD. The charging station and the vehicle communicate to each other to control the charging process. With a peak current of 80A, the maximum delivered power can be nearly up to 20kW. The SAE’s level 2 is comparable to the IEC’s mode 3.
SAE DC levels: SAE J1772 also defines charging at DC voltages with high currents of some 100 amperes and voltages up to 400V and above. Due to the high amount of electrical power, DC charging allows minimizing charging time and is generally referred to as DC quick charging.
IEC mode 1: Similar to SAE AC level 1 charging, this is charging with AC on a typical household wall outlet, either 1 or 3 phase with currents up to 16A. In this mode there is no communication between the energy source/grid and the vehicle. It must be ensured that some GFI/RCD protective device is installed on the infrastructure side.
IEC mode 2: The difference to mode 1 is basically that there are higher currents and a control and protection equipment integrated into the charger cable (In-Cable Control and Protection Device – IC-CPD). The IC-CPD protects from electrical hazards in case of isolation failures and is defined in IEC62752. In its newest edition the IEC62752:2016 requires a peak current I p of up to 1.5kA in case of short circuits. ZETTLERs newest developments are tailored to fulfil this challenging demand
IEC mode 3: In this mode charging with AC takes place through a dedicated charging outlet which is connected to a stationary charger (or wallbox). Charging is controlled via communication between charging unit and the vehicle. IEC mode 3 charging is based on a special purpose infrastructure to deliver the necessary power.
IEC mode 4: This is charging similar to the SAE’s DC levels. Charging with DC is useful when charging with a high amount of power. In IEC mode 4 there is a dedicated wallbox with fixed charging cable and a dedicated DC charging plug.
The ‘ZETTLER Advantage’
As electro vehicles will have a significant impact in future personal mobility and public transportation, we have continually expanded our line of relays and contactors. These state- of-the-art ZETTLER components have been successfully integrated by manufacturers of charging equipment.
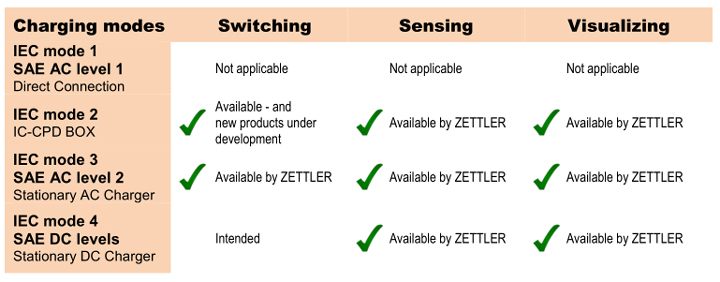
Today, ZETTLER’s product line of AC circuit Relays and Contactors spans across an extended range of product characteristics which make them suitable for many demands in EV charging. These products are accompanied by AC current sensing transformers and HMI solutions of our AZ-Displays subsidiary.
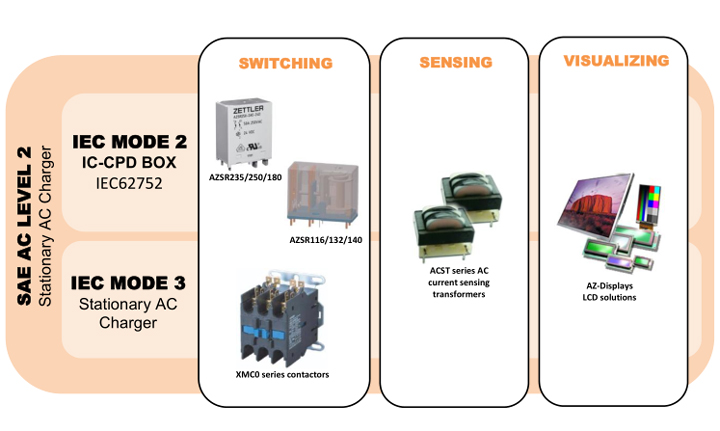
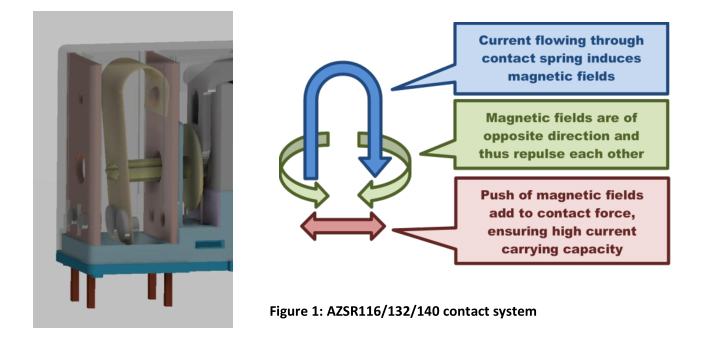
Withstand highest momentary currents with special contact arrangements
In the AZSR116/132/140 series the conventional contact spring arrangement is replaced by a patent pending 1) solution to survive highest momentary currents, as they may occur on short circuits. Through this special arrangement the contact performance even increases due to magnetic force; thus ensuring an outstanding reliability without contact welding.
On the AZSR140 this approach allows 40 Amp switching current and an up to 1500 Amp of short circuit current (carrying) without welding. With its low holding power of only 200mW (also suitable for PWM), this PCB relay has entered a dimension that was hardly imaginable just a few years ago.
Fulfilling safety and supervisory demands with contact monitoring
Additionally the AZSR116/132/140 features a potential free N.C. (1 Form B) monitoring supervisory contact as required by IEC62752:2016, thus making these types of relays ideally suited for applications with high security and safety demands. Contact welding or malfunction can thus be easily detected and indicated.
For more details and information visit http://www.zettlerelectricvehiclerelays.com/
The content & opinions in this article are the author’s and do not necessarily represent the views of AltEnergyMag
Comments (0)
This post does not have any comments. Be the first to leave a comment below.
